
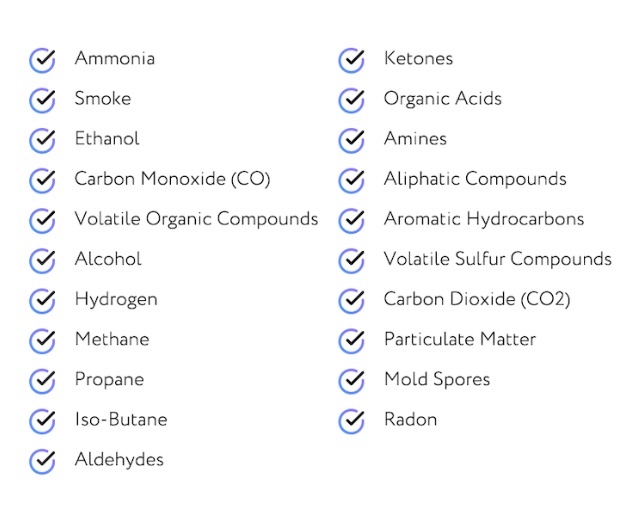
IAQ measures more than 20 potentially harmful indoor air pollutants in addition to ambient temperature and humidity. Exactly what pollutants does IAQ measure? Here’s a rundown.
Smoke and CO
While most American homes already have smoke and carbon monoxide detectors, IAQ offers a smart version which can alert you when you’re away.
Particulate Matter
IAQ provides a sensor specifically for particulate matter (PM) including dust, dirt, smoke, soot, and moisture. These are important to track because small airborne particles (<10μm) can get deep into your lungs and even into your bloodstream.
At worst, particulate matter can cause short term effects such as eye, nose, throat, and lung irritation, coughing, sneezing, runny nose and shortness of breath. It can also worsen asthma, lung cancer, bronchitis, and heart disease. Both acute and chronic ambient PM exposure have been associated with an increased risk of premature death. [Source]

Carbon Dioxide
IAQ also measures for carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is a naturally-occurring gas but also can be an asphyxiate. This means high levels of CO2 can displace oxygen and cause fatigue, trouble sleeping, dizziness, or headaches. Loss of mental acuity has been observed
At concentrations above 1.5 percent (15,000 ppm), CO2 can lead to loss of mental acuity. [Source] Without adequate ventilation, CO2 levels in occupied buildings often rise throughout the day.
Temperature, Pressure, Humidity
IAQ sensors also take discrete temperature, pressure, and humidity readings. These factors can exacerbate or intensify other pollutants that may be present.
Surveys of homes in North America reveal that nearly half of all structures have damp conditions that encourage the growth of biological pollutants like mold, dust mites, pet dander, and pollen. This percentage is even greater in warm climates. The EPA recommends maintaining low indoor humidity, ideally between 30-50%. [Source]
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
IAQ has sensors for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs). These are umbrella categories that consist of a wider range of potentially toxic chemicals.
Concentrations of many VOCs are consistently higher indoors (up to 10x greater) than outdoors, even in locations with significant outdoor air pollution, including petrochemical plants. A wide array of products in the home release VOCs, including paint, solvents, wood preservatives, aerosol sprays, cleaning supplies, automotive products, air fresheners, dry-cleaned clothing, makeup, and pesticides. [Source]
Radon
IAQ will also test for radon. Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas produced by the breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, and water. Because of the difference in air pressure inside your home and in the soil around your home’s foundation, your home acts like a vacuum, drawing radon in through foundation cracks and other openings.
Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer for non-smokers and the second leading cause of lung cancer overall. The Surgeon General and EPA now both recommend testing for radon in the home periodically. Without measurements, there is no way to tell whether radon is present because it is a colorless, odorless gas. [Source]
What Pollutants Does IAQ Measure? (Complete List)
Support our mission to raise awareness of indoor air quality by getting an IAQ today.







